浮动布局的优势在于灵活,却无法实现精确定位,很多布局效果无法实现。
css 定位(css position)可以实现精确定位网页元素的位置。当把元素的 css 属性 position 配置为非 static 后,我们称此元素为 定位元素 。定位元素 可通过设置坐标值 left、top、right、bottom 来精确控制元素在文档中的位置。
position 属性值
static
静态定位是自然流元素,是position 的默认值,表示按照文档流顺序定位元素,不能通过 left、top、right、bottom来改变元素位置。
relative
相对定位,不脱离文档流,可以通过修改坐标值来调整元素位置。
坐标值的参考物为元素的原始位置。
absolute
绝对定位,当绝对定位元素设置了坐标值后,该元素才会在对应方向脱离文档流,否则不会脱离文档流。
坐标值的参照物为离其最近的为 定位元素 的父元素。
如果绝对定位元素只设置了 absolute,而没有设置坐标值时,则该元素没有脱离文档流,其位置依旧会被直接父元素所影响。下面示例中的绝对定位元素 .child 只设置了 left,所以其垂直方向没有脱离文档流,其位置依旧会受父元素位置的影响。
1 |
|
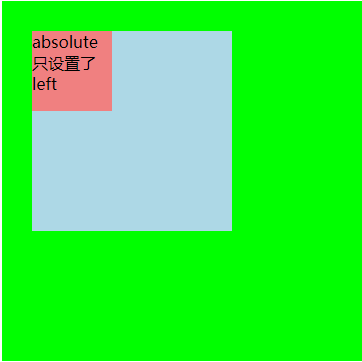
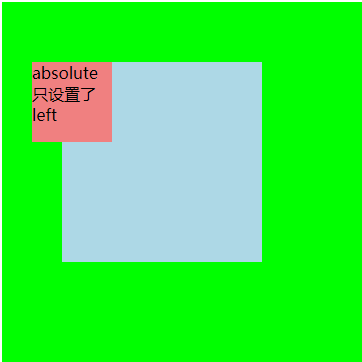
当给其父元素 .wrapper 设置属性 ‘margin:30’ 后,父元素会在垂直方向影响到元素 .child 的位置,因为 .child 在水平方向已脱离文档流(设置了 left 属性),故水平方向并不受父元素影响,效果如下所示:
fixed
固定定位,是绝对定位的特性形式。
坐标值的参考物为浏览器窗口。